Silicon carbide ramming mass is an amorphous refractory material made of silicon carbide (SiC) as the main raw material, combined with high-purity refractory aggregate, fichário, and additives. This material has high thermal conductivity, excellent thermal shock resistance, erosion resistance, e resistência ao desgaste, and is suitable for repair and lining construction of high-temperature industrial equipment, especially for working conditions that require rapid sintering and long-term durability.
Silicon carbide ramming material characteristics
- High refractoriness: temperature resistance can reach above 1600℃, suitable for extremely high temperature environments.
- Excellent thermal shock resistance: low thermal expansion coefficient, can withstand drastic temperature changes without cracking.
- Chemical erosion resistance: good erosion resistance to acidic and alkaline slag and molten metal (such as aluminum and copper).
- Alta condutividade térmica: SiC’s high thermal conductivity (~120 W/m·K) helps to dissipate heat evenly and improve the thermal efficiency of equipment.
- Forte resistência ao desgaste: suitable for high wear areas, such as metallurgical furnace tapping, kiln lining, etc..
- Construção conveniente: ramming molding, suitable for repairing and masonry of complex shapes.
Silicon carbide ramming material introduction
| projeto | índice | ||
| SC30 | SC50 | ||
| Sic % | ≥30 | ≥50 | |
| Bulk density g/cm3 | ≥2.5 | ≥2.6 | |
| Porosidade aparente % | ≤18 | ≤18 | |
| Normal temperature compressive strength MPa | 110℃×24h | ≥60 | ≥80 |
| 1100℃×3h | ≥100 | ≥120 | |
| Heating permanent line change % 1400℃×3h | ±0.3 | ±0.2 | |
| Wear resistance cm3 | ≤6 | ≤4 | |
Application of silicon carbide ramming mass

Metallurgical industry: Repair of linings of electric furnaces, blast furnace tapping channels, ladles, and tundishes.
Nonferrous metal smelting: Linings of aluminum electrolytic cells and copper smelting furnaces.
Indústria química: Anti-corrosion layer of gasifiers and incinerators.
Ceramic/glass industry: Wear-resistant layer of furnace bottoms and combustion chambers.
Others: High-temperature pipes, altos-fornos quentes, and other areas that require rapid repair.
Construction method
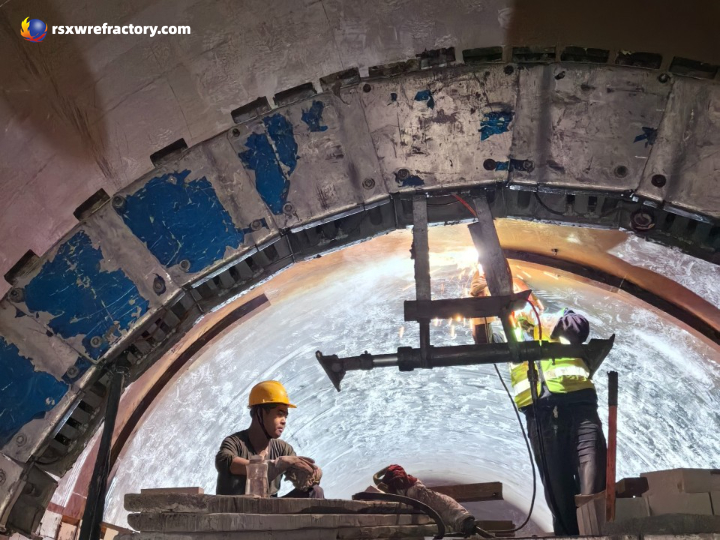

- Matrix treatment: clean the construction surface, remove impurities, and loose layers.
- Mixing and stirring: Add binder (such as water or resin) in proportion and stir evenly until there is no dry powder.
- Ramming and molding: ramming in layers (each layer ≤ 50mm) to ensure that it is dense and has no pores.
- Curing and baking: after natural curing for 24 horas, bake according to the heating curve (avoid rapid heating).
 Grupo Rong Sheng
Grupo Rong Sheng













WeChat
Digitalize o código QR com wechat