The hot blast furnace is a key equipment in the steel smelting process. Its main function is to provide high-temperature air to the blast furnace, thereby improving the working efficiency and production capacity of the blast furnace. The operating temperature of the hot blast furnace is usually as high as 1000°C to 1300°C, so high-performance refractory bricks are needed to protect its lining to ensure its stable operation and long life in a high-temperature environment.
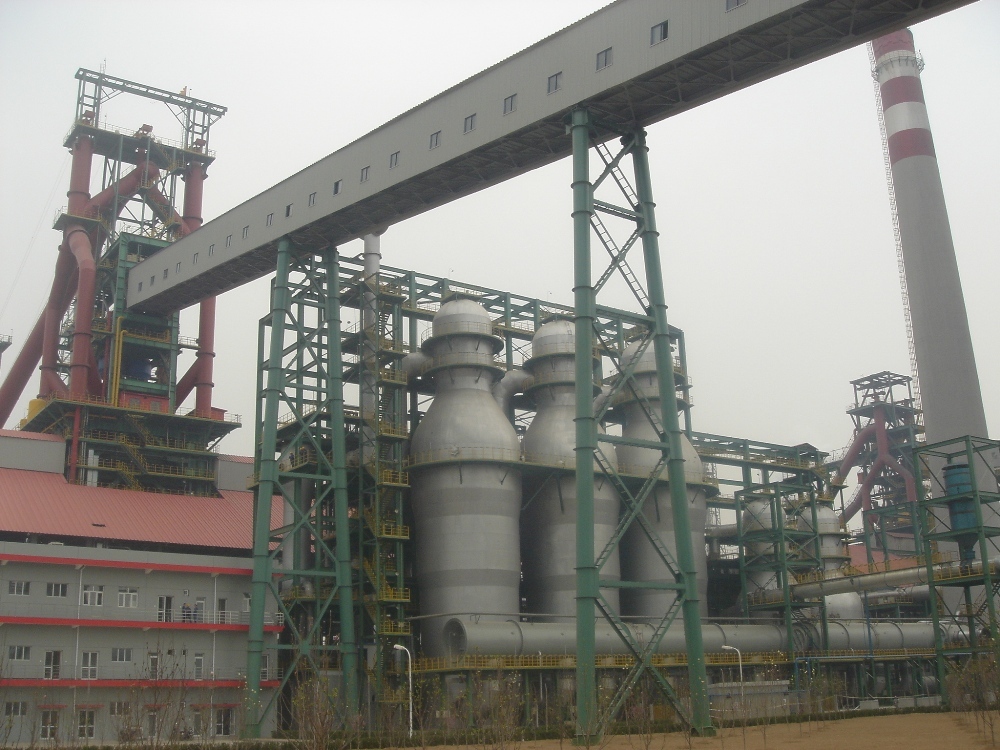

What are the requirements for refractory materials in hot blast furnaces?
A blast furnace hot blast stove is a regenerative heat exchanger, which is a thermal equipment that heats the air blown into the blast furnace from room temperature to high temperature. Its working air temperature is generally around 1300℃. In addition to considering the volume density and specific heat capacity related to heat capacity, creep resistance is still the most important indicator for refractory materials used in hot blast stoves. Thermal expansion resistance and strength, accurate appearance, and no residual expansion are also important indicators.
What are the types of hot air furnaces?
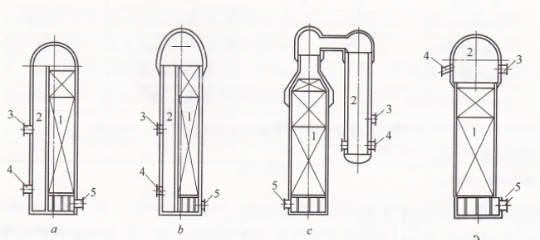
Hot air furnaces can be divided into several types according to the furnace type, such as top-fired, internal combustion type, external combustion type, etc.
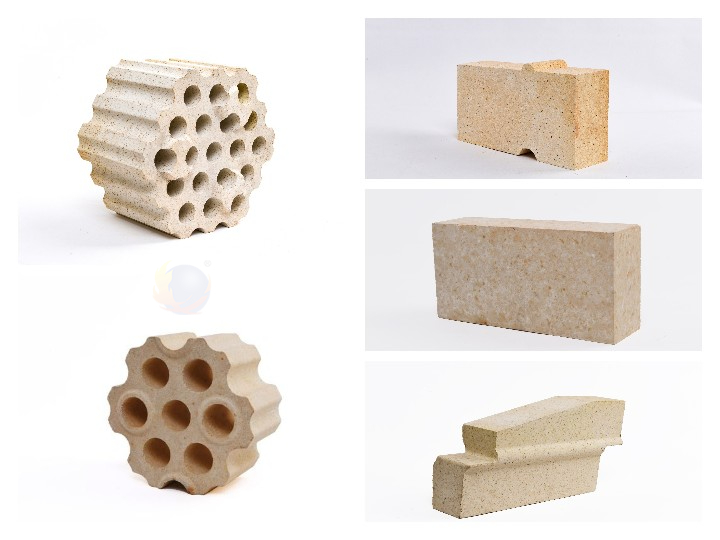
Introduction to refractory bricks used in hot blast furnaces
1, the lower part of the heat storage chamber: clay brick, heat-resistant concrete
2, the middle of the heat storage chamber: low creep clay bricks, high alumina bricks, low creep high alumina bricks
3, the upper part of the heat storage chamber: low creep high alumina bricks, silicon bricks
4, combustion chamber: low creep high alumina brick, silicon brick
5, burner: clay brick, cordierite – mullite brick
6, hot air duct: low creep high alumina brick

 Rongsheng සමූහය
Rongsheng සමූහය

WeChat
wechat සමඟ QR කේතය පරිලෝකනය කරන්න